I am going to inform you about space colonization.
This concept means, human habitation outside the earth.
There are other names for space colonization including, space humanization, space settlement, space habitation.
Which is the long term goal of national science programs.
Nasa administrator Micheal Douglas Griffin said,
“ the goal isn’t just scientific exploration, it is also extending the range of human habitat out from earth as we go forward in time. In the long run a single-planet species will not survive. If we humans want to survive for hundreds of thousands or millions of years, we must ultimately populate other planets. ”
To reinforce this contention, I am going to show you a statistics chart of world population growth. This chart shows how the human population growth exploded after industrial revolution, increasing from 1 billion in 1830 to 6 billion in 2000.
 (represents the statistics of UN world population prospects 2006)(msu.edu)
(represents the statistics of UN world population prospects 2006)(msu.edu)This can basically mean that our resources on earth will not be enough for humans eventually. If the population growth ratio increases like this.
Let’s turn back to the space.
It is common sense that building colonies in space would require access to water, food, space, people, construction materials, energy, transportation, communications, life support, simulated gravity, and radiation protection.
Scientists’ first plan was to colonize the planets, moons or even asteroids in the solar system. Colonies would be located by proximity to some required resources. For example, There are iron for construction material, water ice deposits in buried beneath soil in the permanently shadowed craters on the moon. There are no clouds or atmosphere to block sunlight for energy in the space. For example, an asteroid called 4554 Amun has about $20 trillion worth of metals. There are tens of thousands of asteroids. And so on.
This still didn’t change as a first plan.
But in last couple of years they started to find out earth like planets in their star system’s habitable zones, in the milky way galaxy. Scientists are guessing that there may be 1 billion of them in our galaxy.
For example, Gliese 581 is the 87th closest known star system to the Sun. Which is located 20.3 light years away from the Earth. The star system gained attention after Gliese 581c the first low mass extra solar planet found to be near its star’s habitable zone was discovered in April 2007. But they decided that it wasn’t habitable because of runaway greenhouse effect and terrestrial planet climate model.
This picture shows what a habitable zone is.
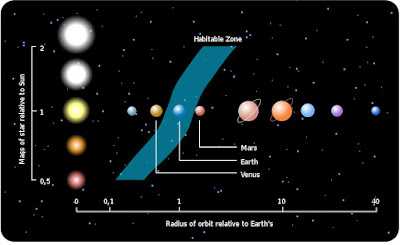
Then they discovered the outermost planet gliese 581d which is firmly in habitable zone. Everything, including liquid water, complex organic molecules and even energy sources to sustain metabolism is possible to be found on this planet. Which can be called life basically. In April 2009, the discovery of exoplanet gliese 581e at the time the closest-known in mass to earth was, announced.
There must be technological developments in order to be able to make that much distance.
First idea that come to mind is to reach light speed or at least almost as fast. But still this will take more than 10 years to go to other star systems with the possibility of a planet in habitable zone.
There are also several serious theories of fast travel. Like using gravitational zones of stars or using worm holes. Etc.
Second idea is cryptobiosis, which means stopping the metabolic procedures by using conditions such as desiccation, freezing and oxygen deficiency. Which is basically stopping our metabolism and turning back to life after required time is passed.
So, after the earth is starting to die, it is either land on moon, mars or some planet close like that. And make it habitable somehow. Or find an earth-like planet in another star system and go there using the developed technology.
Scientists are strictly working on space colonization and it is not impossible to turn that idea into reality.
Thank you for listening.

No comments:
Post a Comment